- LongWood
Transkript
You cannot step twice into the same river: the transformation of Central European temperate forest communities over the past century Radim Hédl, Markéta Chudomelová, Martin Kopecký, Martin Macek, Vladan Riedl, Péter Szabó, Jan Šipoš, Ondřej Vild „You cannot step twice into the same river“ (in a place of an ecological theory, 2500 years old) Παντα θει – Everything is flux (Heraclitus) Studying vegetation dynamics • focus on temporal changes • focus on variation between sites • carefully make some generalizations fauxphilnews.wordpress.com/ 2012/10/17/heraclitus-2012/ Recent environmental changes - habitat fragmentation and loss - changed nutrient balance (surplus of N, acidification) - climate change - biotic invasions etc. Biodiversity decline - decreasing local diversity - biotic homogenization - decreasing functional diversity etc. But really? No net change in species richness resurveys of vegetation plots (usually after several decades) Vellend et al., 2013, PNAS 5-261 years’ resurveys Bernhardt-Römermann et al., 2015, GCB 17-75 years’ resurveys Generally nutrient-richer, shadier forests resurveys, indirect estimation Ellenberg N Verheyen et al., 2012, JEcology Ellenberg L » soil » climate » topography » herbivory » competition » forest management change Biodiversity in temperate forests: focus on the herbaceous vegetation time 2015 The past forest management Historical forest database for Moravia (E-Czech Republic) MS Access, 4 historians entering all possible archival data on forest species composition, management etc. www.longwood.cz Fagus and Picea distribution 11th--19th century archival data Moravia (E-Czech Rep.) 28,000 km2 Source: historical forest database, www.longwood.cz Past forest management Coppicing, 19th century Moravia (E-Czech Rep.) 28,000 km2 Source: historical forest database, www.longwood.cz Past forest management Coppicing, 18th century Moravia (E-Czech Rep.) 28,000 km2 Source: historical forest database, www.longwood.cz Coincidence of the 19thc. coppicing and occurrence of species groups Group Asarum europaeum Group Geranium sanguineum Significant factors: - altitude - mollisols - acidic cambisols NOT coppicing Significant factors: + coppicing -altitude NOT soils Moravia, E-Czech Republic, 28,000 km2 Re-survey of forest vegetation plots in the Czech Republic • potentially ca. 50 thousand „historical“ plots 1930s–1980 • resampling started in the early 1990s • mostly forestry typology survey (1950s–present) Semi-permanent plots (approximate location by map, coordinates etc.) • Database of resurveyed forest plots www.longwood.cz 1953 2004 Distribution of plot altitudes 1000 altitude (m asl.) Current analysis • 15 localities • 1806 samples / 903 plots • old samples 1953-1978 • resampling 2002-2014 • altitude 165-950 m asl. • plot size 400–500 m2 800 600 400 200 0 0 200 400 600 included other 800 1000 Change between the surveys • 15 localities, 1806 samples • 1953–2014 • altitude 165-950 m asl. species richness Boří les lowland Hodonínská Dúbrava Bzenecká Dúbrava Kapánsko Polabí Milovický les Krumlovský les Ždánický les upland Děvín Chřiby Středohoří-Lovosice Středohoří-Litoměřice Bílé Karpaty Rychlebské hory highland Velká Javořina -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 No. species per plot (mean, SD) Change between the surveys • 15 localities, 1806 samples • 1953–2014 • altitude 165-950 m asl. EIV nutrients Boří les lowland Hodonínská Dúbrava Bzenecká Dúbrava Kapánsko Polabí Milovický les Krumlovský les Ždánický les upland Děvín Chřiby Středohoří-Lovosice Středohoří-Litoměřice Bílé Karpaty Rychlebské hory highland Velká Javořina -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 Plot-wise change (mean, SD) Change between the surveys • 15 localities, 1806 samples • 1953–2014 • altitude 165-950 m asl. EIV light Boří les lowland Hodonínská Dúbrava Bzenecká Dúbrava Kapánsko Polabí Milovický les Krumlovský les Ždánický les upland Děvín Chřiby Středohoří-Lovosice Středohoří-Litoměřice Bílé Karpaty Rychlebské hory highland Velká Javořina -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 Plot-wise change (mean, SD) Change between the surveys • 15 localities, 1806 samples • 1953–2014 • altitude 165-950 m asl. EIV moisture Boří les lowland Hodonínská Dúbrava Bzenecká Dúbrava Kapánsko Polabí Milovický les Krumlovský les Ždánický les upland Děvín Chřiby Středohoří-Lovosice Středohoří-Litoměřice Bílé Karpaty Rychlebské hory highland Velká Javořina -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 Plot-wise change (mean, SD) Change between the surveys • 15 localities, 1806 • 1953–2014 • altitude 165-950 m asl. Beta-diversity old survey new survey mean dissimilarity „Sensitive“ species Uncommon but sensitively indicating long-term environmental changes 16 spp. 15 spp. 5 spp. y-axis: % of all occurrences in old or new surveys note the scaling differences images source: commons.wikimedia.com Invasive species: focus on Impatiens Other possibly important factors: - soil texture / moisture - disturbances Conclusions • Species diversity consistent with the existing studies, no net change in species richness. • Invasive species increased, orchids and wintergreens decreased. • Environmental changes consistent with previous studies (nutrients, light, moisture). • No pattern along altitude/forest management was observed. Ongoing research: getting more detailed explanatory data • plot/site–wise data on management history • better data on abiotic environment (soil, light, deposition etc.) • inclusion of species traits Historical management as explanatory factor For each (re)survey period • management form • tree species composition • forest stand age • intensity of the most recent cutting • stand density / tree volume • non-forestry uses • game density and composition Two periods: - medieval to 1850 - 1850 to present Creating a historical-ecological database of resurveyed forest plots Management, level 1: prehistoric to 1850 Management, level 2: 1950–present Environmental influences: deposition, temperature… Thank you The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Research Council under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) / ERC Grant agreement no 278065. www.longwood.cz
Podobné dokumenty
Publications of Radim Hédl Peer-reviewed papers 2015 Bernhardt
 vegetation and microbial linkages with slope aspect in a montane temperate hardwood
forest. Ecosphere 5(5): art66. doi: 10.1890/ES13-00379.1
Hofmeister J., Hošek J. & Hédl R. (2014): Edge-efect as ...
vegetation and microbial linkages with slope aspect in a montane temperate hardwood
forest. Ecosphere 5(5): art66. doi: 10.1890/ES13-00379.1
Hofmeister J., Hošek J. & Hédl R. (2014): Edge-efect as ...
Srovnání hlavních genetických taxonů hlavních klasifikačních systémů
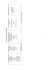 Taxonomický klasifikační
systém půd
České republiky
Referenční třídy
Typy
Subtypy
Variety
Subvariety
Substrátové formy
Ekologické fáze
Degradační fáze
Taxonomický klasifikační
systém půd
České republiky
Referenční třídy
Typy
Subtypy
Variety
Subvariety
Substrátové formy
Ekologické fáze
Degradační fáze
Coppicing in the 19th century
 Restoration of coppicing management in
Devín: can a biodiversity decline trend be
reversed?
Radim Hédl,
Markéta Chudomelová, Martin Kopecký, Jana Müllerová,
Vladan Riedl, Péter Szabó, Jan Šipoš, On...
Restoration of coppicing management in
Devín: can a biodiversity decline trend be
reversed?
Radim Hédl,
Markéta Chudomelová, Martin Kopecký, Jana Müllerová,
Vladan Riedl, Péter Szabó, Jan Šipoš, On...
jak chránit motýly a brouky zároveň? smířlivé zamýšlení po třinácti
 KONVIČKA M., KURAS T. (1999): Population structure, behaviour and selection of oviposition
sites of an endangered butterfly, Parnassius mnemosyne, in Litovelské Pomoraví, Czech
Republic. Journal of...
KONVIČKA M., KURAS T. (1999): Population structure, behaviour and selection of oviposition
sites of an endangered butterfly, Parnassius mnemosyne, in Litovelské Pomoraví, Czech
Republic. Journal of...
napoleon bonaparte - Základní škola Tatenice
 Francii válku
• Říjen 1805 – poráţka francouzskošpanělského vojska u mysu TRAFALGAR
• Padl zde admirál Nelson
• 2. prosince 1805 BITVA TŘÍ CÍSAŘŮ
• U SLAVKOVA
Francii válku
• Říjen 1805 – poráţka francouzskošpanělského vojska u mysu TRAFALGAR
• Padl zde admirál Nelson
• 2. prosince 1805 BITVA TŘÍ CÍSAŘŮ
• U SLAVKOVA
zde - CZ-IALE
 výrazně reflektuje historickou strukturu krajiny. Výsledné pattern je přitom nejlépe vysvětlitelné
migračními schopnostmi jednotlivých druhů. Zjištěná migrační rychlost se pohybuje od 1,2 m/rok
(Im...
výrazně reflektuje historickou strukturu krajiny. Výsledné pattern je přitom nejlépe vysvětlitelné
migračními schopnostmi jednotlivých druhů. Zjištěná migrační rychlost se pohybuje od 1,2 m/rok
(Im...
 Velká Javořina
Velká Javořina
 ZÁPLAVY A SESUVY PŮDY
ZÁPLAVY A SESUVY PŮDY

