integrovaný programový prostředek
Transkript
The use of hydrological system AquaLog for flood warning service in the Czech Republic Jakub Krejči1) , Jiří Zezulák2) 1) 2) Aqualogic Consulting Czech Agricultural University, Czech Republic Introduction AquaLog CHMI Hydrological Forecasting System Since mid 1990’s, the hydrological modeling system AquaLog became of service to the Czech Hydrometeorological Institute (CHMI) ´office´ procedures in real-time flow forecasting in whole Elbe river basin. The models have been already installed for catchments, river network and reservoirs of the Elbe basin, including Vltava, Ohre, Berounka, Sazava, and Jizera rivers and Becva catchment, which is part of Morava river basin. The software empowers step-wise strategies in forecasting system implementation. In this manner, the structure of models already completed and operational is being gradually propagated to entire Elbe system, from its headwaters to downstream. Upon they become fully operational, the models are integrated into a single entity of the Elbe forecasting system. AquaLog was designed to be a modular system that contains a variety of modeling techniques and utilities and allows the user simulate the following hydrological processes: •snow accumulation and ablation •rainfall-runoff processes •river routing •simulation and control of reservoirs AquaLog provides for solution in a several distinct computational options: Calibration, Parameter optimisation, Simulation and Forecasting. Under a compact AquaLog GUI shell a user can make use of three categories of modeling techniques accommodated in its library group of hydrological routing models •TDR transport - diffusion analogy •MC Muskingum-Cunge •FLD tree-shaped or looped system of interconnected river branches based on full solution of St.Venant system by a implicit scheme (according to US NWSRFS) •SLF self-tuning auto regressive techniques for real time forecasting of stage, discharge •group of hydrological catchment models •SNOW 17 snowmelt simulation (according to US NWSRFS) •APIc the Antecedent Precipitation Index Continuous model •SAC-SMA Sacramento model (according to US NWSRFS) •group of interactive simulation of hydraulic flow-control units •MAN kinematic reservoir equation, controlled spillways and bottom outlets, power hose discharge and transfer of watery fee-flow channels The CHMI guaranties the regional-scale hydrological forecasting through the Czech Republic. When- and wherever the man-supervised flow-control becomes of concern, the Institute collaborates with respective River Boards. In the Elbe system, the regional forecasts are issued daily for 54 water gauging sites (forecasting points). The forecast lead time ranges from several hours up to one day. CHMI produce hydrological forecast of 2 days lead time (1h time step resolution) for catchments of size from about 100 km2 up to large basins of several thousands of km2. Due to geographical position of the Czech Republic, the main uncertainty of the forecast in the head water basin is caused by inputting quantitative precipitation forecast (QPF) and also by quantitative temperature forecast (QTF) in the winter and spring snow melting period. QPF and QTF of NWS ALADIN computed at CHMI input va Vlta Smedá -V IS LP RED 20 32 L29 1 20 01 90 01 78 e Metuj LI0 LJ6 LI1 0 0 20 Zd ob Ro nic e ky ten ka L50 LJ Kn 8 ìž ná 0390 LN L5 6 0 LN Bì 3 lá Havlí čkův Brod Ma 10 13 ic e LL1 3 árk a L ásenice Y # 12 7 0 Ne ž Římov VD Římov 2 MARI LM LT 1 EH RE Br a un ab ach 11 Dolní Ostrovec Písek La ins itz 25 Y # HO Ehrendorf L È e M6 L ičov 7 rn L M á LM8 á 1081 en Vlta va Studva VD Lipno V lta V LL1 LL6 Vyšší Brod 10 90 Hoheneich HE L L9 Mal LP0 še LM0 11 26 Pořešín 1070 Vltav a Len ora LP 6 Chlum 1 Tepl á Varvažov #Y LL8 LM nice 2 LM 3 1150 119 0 L už 1110 Pilař Roudné 4 LP 2 LM 1130 M Orlík 11 51 České Budějovice Březí 10 60 L57 L38 80 5 LN Otav a L68 1390 L64 Lu žn Volyòk a L66 LL L P4 14 70 1480 Černý Kříž 1 L H2 LK 8 LH L54 20 80 L1 5 L35 Blanice 32 VD Husinec 1 LP Klatovy 0 LK Chrud 0 Hamry imka 4 LL V ydra Heřmaň 1500 Poded vory Staňkov LG0 04 052 0 16 72 L36 15 39 1533 Přemilov LL2 Bech yně L L0 BLHU LL7 04 9 Klenovice 10 15 e nic Bla 1 L6 L56 1380 Otava L58 Nemětice 1430 Slatina 04 L34 L11 16 1546 1537 1879 Úhl ava lé L abe LA 2 era L3 0 0850 08 60 LK 5 Jav or ka 6 L0 2040 J iz LB Mrli 7 na LK 90 21 B erounka L83 2 L8 L73 L77 1801 2 LQ4 1900 Teplá L7 Litavka L85 LR 1 7 L8 L76 Katovice 1350 Y # L B ys K3 tøice 00 09 Svitá vka L V3 LV 1 2 400 L22 be L21 La L02 03 21 60 L9 0 Oh ø e L5 a v Ota Sušice Modrava Y # 0491 Sáza va LP3 Y # Kolinec Y # Katovice Sušice #Y # Stará Lhota Y Y # Heřmaň Y # Nemětice Y # Bechyně Y # Klenovice Y # an ice 1 Vl tava Bl VD Bystřička Y # Modrava #Y Podedvory #Y Lásenice Y Husinec # České Budějovice Y # Vsetín Y # Y # Y # VD Karolinka Lenora #Y Březí Y # Černý Kříž #Y #Y Chlum Ústí Y # Y # Y # Římov Y # Lipno#Y Pilař-Majdaléna Roudné Pořešín Mal š e FREE SUPLEMENT. WATER UHNY 0300 nad Kněžnou L2 0 Chlístov Písek 1410 L65 Týniště 0240 L6 9 7 0 038 Kolinec Stará Lhota VD Nýrsko 4 Čenkov 01 80 Y # L4 1 0 Novoh rádka 0 58 CRSV LH8 L 19 ZESV VD Orlík 1330 Y # Os tr LL užná 5 1820 5 L7 Nová Huť Y # Y Klabava # Stříbro VD České Údolí #Y #Y Koterov Lhota #Y #Y Stěnovice Bílá Hora #Y LJ VD Hracholusky 6 LH3 LN 7 Dolní LN Ostrovec om nice 152 L 0 Rych nov L40 LG 7 7 15 30 15 S kalic e N8 Chábory 6 LH 58 15 Y # 16 V LOR Varvažov L Hamry Soutice 1656 V LKA Z ruč Dì dina Mitrov 5 Úh řetice VD Seč L18 61 16 0210 LH Hradec O Králové rli ce Svídnice LH Louňovice VD Kamýk Koterov 18 70 Klatovy Y # 16 Libež 59 Jaroměř 52 LN4 Paří žov L16 Radonice a L37 Chotýšank Radíč G1 Y # Krčín PRRO LG4 LG3 LG5 ná uè Lo 30 VD Slapy Mas tník 38 Hrachov 1 5 Brzin a tuje Me Staň kov Nesp eky 0148 Zlíč 60 L J5 18 ## Y Y Liblín V LSL 01 065 0 S ázava 3 VD Král ovství L La 53 be Přemilov#Y M aršov nad Metují Hronov 70 04 B e1 860 ro un k a Bílá Hora L8 0 VD RACU České Štěnovice Údolí 1799 Labe 066 0 L14 L13 4 15 VLST Ú pa uza db 4 R a L7 Čen kov 1 960 Slatina n/Ú. 1 LG be La L70 Stříbro 17 4 0 Klab avaVD Klabava Nová Huť LQ 5 KLKL Štěchovice (Kocába) VD Štěchovice 2 LG LQ2 L08 Ž leby Zbraslav 2 LQ1 Beroun LC LC1 a brav LQ Liblín 1910 Støela ka un ro L10 Be VLVE Beroun D ou Plasy VD Hracholusky Mž e 1980 3 LQ L 17 Y # 0820 Chuchle L8 4 ka ro un Be 6 ka Želiv Beroun Plasy Sány 0060 Jaroměř 0170 øe víè Velký 01 41 Dřevíč Svídnice VD Seč #Y 0 n/Zdob. 0 31 Žamberk 0270 02 Klášterec Často lovice 55 L4 Kostelec Němčice 0370 L55 4 LN2 L42 PRPA 80 L 06 02 VD Pastviny Orlice N1 Malá Čermná 10 Div oká Nekoř LG Přel ouč 6 0 360 9 LG 0250 LH0 034 Dašice L45 0 LG8 Dolní Lib chavy Nemošice Cerekvice Tichá Orl ice Ústí n/Orl. LJ9 0590 03 50 LM9 0450 10 16 LQ7 LJ2 S TZL 1761 50 17 MZHR VD Lučiná na LK6 D Horní Staré M ěsto 0 Opato vice Plaňany Trpísty 95 16 L25 1 LK 2109 00 08 Cidli 0140 42 Rohoznice 0 VD Jesenice 2065 LX5 L po om tok nic ký VD Žlutice 9 1 88 S tøela 07 50 00 Deb rné 0 70 LX3 T epl ička LX1 L24 Stanovice Nový Bydžov Vestec LB5 LB8 0 LC Cheb VD Skalka 07 70 Nymburk 7 Březo vá e L 86 Oh ø L9 5 8 Před měřice 1040 9 LB 2060 2 073 101 L3 1 Brandýs Prosečné 0710LALK L ázně Běloh rad LK 2030 1 Vraň any L3 2 va V lta 0690 a lin C id 4 LK Žatec Mělník Louny L97 LJ 3 Vestřev 0 05 Cerekvice Y # Y # Horní Maršov 0030 L5 Oleš ka 0 LA8 6 ka Výrov LB6 LX4 LV 8 2 LA era 21 01 Stará Role LV L V6 2 L9 e Ohø L0 3 Stranná VD Nech ranice LX2 e Lab 08 L88 0678 Jičín 409 42 240 L91 L98 9 5 0870 409 Klášterec 21 45 L9 Ostrov LA Slaná L04 va 2 4 Karlo vy Vary 2140 Svatava L V5 L8 9 LV 7 Citice Calibrating system Ensemble Streamflow Prediction Y # Ličov Y # Vyšší Brod Statistics Probability forecast Operational forecasting system Hydrological models Verification Preprocessor of meteorological ensembles Hydrological Ensemble Processor Products Generator Data Assimilator Products MODS, Updating, Optimalization of initial conditions Interactive forecasting program Precipitation and Temperature ensembles Weather Generator Historical data Method was originally inspired by ESP US NWS procedure, however because of using deterministic hydrological forecasting system the aim was to reduce number of ensembles. There is not enough historical meteorological data (since 1961) to apply simply random selection of few years from the historical dataset; therefore LARS-WG generated long time series were used instead of historical observation of precipitation and temperature. MAN – interactive reservoir control Hluboká 01 Inflow CO00 Zvíkov Orlík Koloděje RES CC 900.00 800.00 Discharge CKEL DMY LL 06 05 RE S EE Slapy DMY DD Mastník C223 Brzina C222 04 VD KAMÝK Pool HKRE elevation (m asl) Kamýk 700.00 Pool HSRE 400.00 Vrané 300.00 100.00 400 300 200 100 DMY FF VD SLAPY 0 distance (km) Pool HTRE 09 11 Discharge CTEL DMY MM 10 RES II Modřany Discharge CSEL 08 RES GG Orlík 500.00 07 DMY HH Štěchovice VD ŠTĚCHOVICE 600.00 200.00 Flood 1890 Děčín Discharge COEL 03 Orlík AquaLog provides export of forecast to the WEB sites and to the special client program ALView. Simulation characteristics • Interactive versus non-interactive • Modifications of processed input data • Optimalisation of initial conditions (Rosenbrock) • Modifications through special adjustment runtime parameters • Temporary modification of parameters • Updating of forecast Nash Statistics Hourly, Daily and yearly basis Sutcliffe DMY BB 02 Zbraslav Pool HVRE 354 352 350 3000 348 2000 346 1000 344 time Models •Reservoir •Rating curve •Spilway •Bottom outlet •Power generator •Release 324 304 284 264 244 224 204 184 164 144 124 104 84 64 44 24 4 -16 -36 342 -56 0 stage (m ) 4000 Petri-net algorithm offers a powerful tool for decomposition of a system and for subsequent userindependent numerical simulation DMY JJ Berounka C190 5000 356 VD VRANÉ dam inflow dam outflow DT=X1..X10 discharge - Prague optimal discharge sub basin inflow dam water stage 6000 12 13 DMY ODTOK KK Reservoir optimization control discharge (m 3.s-1) Optimalisation of SAC-SMA initial conditions using different optimalisation criteria to adjust simulated hydrograph to observed discharge time series. •Temporary modification of parameters Modification of initial snow water equivalent (SWE) for snowmelt model is performed quite often in spring months if measured and calculated SWE differs significantly. Manual changes of initial condition is made trough MODS module. BASEF changes the recessing base flow amount in base flow MFC changes the melt factor correction value for SNOW-17 SACBASEF multiplies the base flow runoff from the SAC-SMA SACCO changes the SAC-SMA soil moisture carryover values UCBASEF change the constant base flow amount for IUH UHGADJ - modifies a unit hydrograph with horizontal and/or vertical adjustment factors UHGCHNG changes the ordinates of a unit hydrograph WECHNG changes the value of snow water equivalent PXADJ multiplies the input rain data by a constant PXADJ adds number of degrees to temperature data Pool HORE Controlled variable VD ORLÍK Týn Optimized and original hydrograph. Initial conditions of SAC-SMA model optimized by automatic optimisation using Rosenbrock optimisation scheme. Moldau Cascade Písek RES AA Hněvkovice Kocába C224 Nespeky C226 Run time modifications represent temporary adjustments to time series or initial conditions. The forecaster uses MODs at forecast execution time to adjust these values in an attempt to improve the results of the forecast model computations. MODs are available for making temporary or, in a few cases, permanent changes to selected parameters. •Modifications of processed input time series Modification of PXADJ – Input precipitation is multiplied by PXADJ parameter based on radar data and other information. Modification of TXADJ –input air temperature may be adjusted by change of TXADJ, usually when it rains and air temperature is close to 0 °C • Optimalisation of initial conditions SACRAMENTO and SNOW-17 initial condition are kept from previous simulations to keep continuity of soil saturation and characteristics of snow. AQUALOG uses automatic Hněvkovice Calibration Characteristics • Performs computations for few forecast points for many time steps. • Long time series • Compatible with operational system. • Produces graphical output for manual calibration. • Includes algorithms for automatic optimisation Applications: • Historical watershed simulation • Reconstruction of historical events, scenario analysis • Model calibration Optimisation schemes • Rosenbrock • Pattern search • Shuffled complex evolution Convergence criteria – different criteria available • Daily RMS error • Nash-Sutcliffe • Pearson coefficient of corelation • Multi-Step Automatic Calibration Scheme MACS České Budějovice Run-Time Modification Lipno Calibration and Simulation Observed Time Series Controlled discharge Radar And Remote Sensing Precipitation + Temperature forecast LABE Automatic Observing Stations Hydrological and hydraulic models Štěchovice Vrané Modřany Analysis and data processing; Praha Operational database Kamýk Network of Voluntary Observes Hydrological And Hydraulic Models Slapy Professional Observing Stations Database of Model Parameters Short time deterministic hydrological forecasting has became a standard real time practice The experience from recent flood events in the Czech Republic proved the increased forecast user demands for the longer lead time of the forecast and some probabilistic interpretation of forecast outputs. Longer lead time hydrological forecast is necessary for effective water management of reservoirs to successfully combine their different, often antagonistic, purposes such as the flood protection on one side and water supply and hydropower generation on the other hand. However with prolonging lead time the need of probabilistic expression is increasing what was proved by common evaluation of QPF uncertainty as well as by some case studies of QPF and QTF impact on real time hydrological forecast. Kořensko International Exchange of Data(ECMWF, ALADIN etc.) Historical database Historical Data Analysis Forecast Dissemination 1 7 L 0 iz era J 0980 Štěpanice Jizerka 4 LA3 LA Probabilistic Forecast Automatic interface between primary real-time data collection system including archiving of the passed data and the modeling and forecasting system. Provides for both automated and mansupervised data pre-processing and quality control, using graphical and statistical data-validation procedures. Consists of set of procedures, that are used as the tool in analysis and pre-processing of raw climatological and hydrological data to update time series used in forecasting by AquaLog. • historical and operational data collection -input of regularly observed data from data collection systém (stations, radar etc.) -input of forecasted data (QPF by ALADIN and ECMWF) • database management, including the data validation, primary and secondary data processing system (validation, screening reconstruction and missing data entry • graphical, tabular and statistical tools for primary processed data and their validation in manual or automated mode • methods of supplementary processing and analysis of time series • creation and maintenance of station files (characteristics of meteo- and hydro- stations) • topographical representation of the basin, river system and location of the stations based on GIS generated data Y nice S TRAZ 091 0 LR3 Stráž p .RalskemŽ elezný Brod Dolní LA6 Sytová Mimoň 02 5 L0 Sv ata Data processing - AquaBase Inverse Distance Weights (number of stations, max. distance, exponent) • Inverse Distance Weights – QUADRANTS • Kriging and Co-Kriging – (http://www.gslib.com/) • Thiessen Polygon Network Input Formats: ESRI ASCII Grid, GeoEAS, ESRI shapefile Export Formats: HEC-RAS (DSS-VUE),CSV etc. Conversion utilities WGS-84, UTM, S-42 and S-JTSK 2322 Harrach ov 0010 LK Mu Špindlerův Mlýn 9 mla va 00 20 45 LALA 08 Jablo nec VD Labská 0 n.Jiz. 13 Dolní 0 J iz 2350 P louè AZ Bohuňovsko-Jesenný L V2 Česká Lípa S TR Z ákupy LA7 022 24 Byst øice Ro lava Basic scheme of AquaLog system • Josefův Důl 2340 LV 0 23 90 P lou ènice Aqualog system consit of main modules, AquaLog itself and AquaBase, SOLWIN, AquaESP, Mods, Manipul and ALVIEW. Methods of MAP, MAT, MAE (Mean Aerial Precipitation, Temperature and Water Equivalent) 08 30 0880 Benešov n.Ploučnicí Vltava Y # L2 3 L0 9 Dluhonice O Děčín Bakov Trpísty 2 F rýdlant Bílý Potok R YD -BP LF 3230 10 22 L26 226 0 Jesenice Rychnov nad Kněžnou Y # Týniště nad Orlicí#Y Y Slatina nad Zdobnicí # Y# # Y Klášterec # Y Častolovice Y Žamberk # Kostelec Y Němčice # Y # Y Nekoř # Přelouč Malá Čermná Y # Y Dašice # Nemošice#Y Y Dolní Libchavy # Y Úhřetice # Y Ústí nad Orlicí # Předlánce FR YD LA Y # I S- 40 Hřensko LA9 Kamenice Y # Cheb Ústí n.Labem ina Trmice Bíl L67 Y # Y # Y Mitrov # 5 LP PERCOLATION Žatec Stará Role Y # # Y Karlovy Vary Svatava Y # Y # Bøezová Citice#Y Y # Teplièka a 2 Y # va V lta WATER Y # Louny 15 34 TENSION 3260 Y # 0 FREE PRIMARY WATER Želivka 32 5 Beč 4 v Y # Chábory Bí lý Pot ok Chlístov Y # Y # 245 BASE FLOW Y # Kelč Y # Višňová LV Y # Valašské Meziříčí Y # Y # Jarcová Rožnov Frýdlant v Čechách Trmice#Y 80 10 BASE FLOW Y # Y # Y # Y # Y # # Y Hradec Králové LP7 LOWER ZONE F Teplice Višňová Y Y# # Y # 73 19 NO FF DIR ECT RUN OF Předlánc e Pařížov Y # Soutice Louňovice Hrachov 80 RU Y # VD Kamýk#Y 18 FLO W CE Y # Radonice Zruč # Y Y # Libež Radíč a lav Ús 1 L7 Probability forecast Scenarios (pseudo – real time) RFA Maršov nad Metují Velký Dřevíč Hronov Y # Y Slatina nad Úpou # Království Y Česká Skalice # Jaroměř #Y Krčín Y # Žleby Y # 9 Deterministic forecast SU Dluhonice Horní Staré Město Y # Prosečné Y # Y Vestřev # Y Debrné # Y # Nespeky Y # L7 UPPER ZONE INT ER 8 Horní Maršov Y # Sány Plaňany Y Chuchle # # Y LQ0 TENSION WATER 9 Špindlerův Mlýn Nový Bydžov Y # Štěchovice 1 Valašské Meziříčí Y # 4 R2 3 2 #Y Rožnov ožno vská Y # Bečv 5 a Jarcová 6 3 Y # 2 1 VD Bystřička 5 a čv 4 3 e áB 2 1 1 4 Vsetínsk 1 3 5 #Y 2 11 12 VD Karolinka 2 1 #YVsetín 7 6 1 10 Y # 13 Ústí 8 5 9 3 4 Y # Y # Nymburk Y # VD Štěchovice#Y VD Slapy 09 18 FREE WATER The Sacramento model represents an attempt to parameterize soil moisture characteristics in a manner that: • would logically distribute applied moisture in various depths and energy states in the soil • would have rational percolation characteristics • would allow an effective simulation of streamflow Rohoznice Y Zbraslav # 1 3 Y # 3 Kelč 1 Labem#Y Brandýs nad 3 6 Teplice Y # Y # Vestec YPředměřice # # Y Lhota Y # Lázně Bělohrad Y # Y # VD Žlutice 6 Y # Mělník Y # Vraňany Y # 4 Harrachov Y # Kbelnice 17 90 Planning, training Y # MZLU 5 Y # Zákupy Y Y # # Y Mimoň # Y Česká lípa Y# # Y Dolní Štěpanice # # Y Železný Brod Dolní Sytová Y # Slaná Ústí nad Labem 01 200 Operational mode Josefův Důl Děčín #Y Benešov Y # 2 7 SAC-SMA scheme Y # 101 AquaLog Catchments are subdivided into zones (1-20). The area of the zone is aprox, 10-40 km2. Each zone has individual parameters. Typical subdivison for Becva catchment. Hřensko 20 21 AquaLog is multipurpose decision-supporting system in field of water management and hydrology and uses methods of deterministic modelling to investigate hydrological and environmental processes in the real and historical data and, possibly, also on artificially generated data. Apart from field of operative hydrology AquaLog can assist as a tool to judge the measures taken in water management processes and scenarios. Scheme of Elbe River flood forecasting system Od rava L9 3 AquaLog The Elbe, Vltava, Ohre, Berounka, Sazava and Jizera river-basins ara subdivided into lesser subsystems. Elbe hydrological model consist of 210 main river reaches, where the transport diffusion (TDR) model is used for channel routing, 173 sub-catchments where the SAC-SMA rainfallrunoff model coupled with ablation and snow-melt SNOW-17 model is applied and 27 dams with forecasted outflow. The model is subdivided at 5 parts, according of regional offices. The models are daily- and continuously operated. Simulation time step is one hour. DMY NN 14 Signal 15 Inflow Scenario Inflow Forecasts Forecast-Decision System Reservoir regulation Policy Forecast/Control Horizon (e.g., 48 hours) System Configuration Regulation Policy Demand Scenario One Hour- Time Step System Simulation Flood Control Outflow Energy Assessment Horizon (e.g., 2009-2012) Six Hour- Time Step System Simulation discharge (m3.s-1) 4500 4000 Observed hydrograph 3500 Simulated for natural conditions Simulated for affected conditions 3000 Water Supply Pool Level Recreation, etc. 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Software HISTORY • Late 1970s the first application on Mainframe (SIMFOR) • Mid 1980s SIMFOR is ported on PC with GUI (OS DOS) • Mid 1990s AQUALOG is a fully MS Windows based application • Mid 1990s AquaBase is added to AquaLog • Mid 2008 AQUAESP is added to AquaLog • Most of the core code is Fortran, GUI is in Visual Basic and VB.NET 0 26.08.1890:00 31.08.1890:06 05.09.1890:12 10.09.1890:18 16.09.1890:00 21.09.1890:06 tim e Contacts: Jakub Krejci [email protected], AquaLogic Consulting, Ltd, Roklinka 224. 25244 Psary, , Czech Republic Jiri Zezulak [email protected],Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Kamýcká 129, 165 21 Praha 6 – Suchdol, Czech Republic Updating of forecast Simulated hydrograph always more or less differs from the observation. Therefore forecast usually doesn’t “start“ at last observed value and have to be update. Automatic updating mode is extended by module UPDATE has been developed for advanced manual updating. It enables complete interactive modification of forecasted hydrograph in every time step. Reservoir Intreractive Module
Podobné dokumenty
celek-resume
 Kryštof Clam-Gallas koupil Obříství pravděpodobně roku 1810 a záhy nechal k zámku přistavět čelní křídlo. Již roku 1817 však sídlo prodal. V současné době vlastní zámek Obříství restituent Igor Hav...
Kryštof Clam-Gallas koupil Obříství pravděpodobně roku 1810 a záhy nechal k zámku přistavět čelní křídlo. Již roku 1817 však sídlo prodal. V současné době vlastní zámek Obříství restituent Igor Hav...
Možnosti využití srážko-odtokových modelů na malých a středně
 lokalizované (české) verze produktů (zde je výhoda či nevýhoda čistě subjektivní), zkušenosti
jiných uživatelů a celková používanost produktu v Česku i jinde ve světě.
lokalizované (české) verze produktů (zde je výhoda či nevýhoda čistě subjektivní), zkušenosti
jiných uživatelů a celková používanost produktu v Česku i jinde ve světě.
URL
 Numerické metody v testovaných softwareových systémech poskytují několik parametrů,
které můžeme specifikovat a které ovlivní výpočet řešení. Naprosto zásadní z pohledu fungování metody jsou tolera...
Numerické metody v testovaných softwareových systémech poskytují několik parametrů,
které můžeme specifikovat a které ovlivní výpočet řešení. Naprosto zásadní z pohledu fungování metody jsou tolera...
k nahlédnutí zde
 Ferebauerová Eva Ing., Palackého 347, 517 54 Vamberk
Frühbauer Aleš, Mírová 1435, 516 01 Rychnov nad Kněžnou
Genzerová Anna, Staročeská 264/4, 165 00 Praha 6
Güllichová Monika, Sluhy 257, 250 63 Pr...
Ferebauerová Eva Ing., Palackého 347, 517 54 Vamberk
Frühbauer Aleš, Mírová 1435, 516 01 Rychnov nad Kněžnou
Genzerová Anna, Staročeská 264/4, 165 00 Praha 6
Güllichová Monika, Sluhy 257, 250 63 Pr...
D.1 - Hodnoty N-letých průtoků a poměru Q 100 /Q a pro vybrané
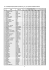 Dolní Libchavy
Třebovice
Hylváty
Ústí n. O. - Kerhartice
Čermná nad Orlicí
Týniště nad Orlicí
Chábory
Mitrov
Hradec Králové
Němčice
Litomyšl
Cerekvice
Dašice
Hamry
Přemilov
Padrty
Svídnice
Luže
Leš...
Dolní Libchavy
Třebovice
Hylváty
Ústí n. O. - Kerhartice
Čermná nad Orlicí
Týniště nad Orlicí
Chábory
Mitrov
Hradec Králové
Němčice
Litomyšl
Cerekvice
Dašice
Hamry
Přemilov
Padrty
Svídnice
Luže
Leš...
 HK Q - - I
HK Q - - I







