BRAF mutation
Transkript
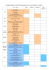
Molecular genetic analysis and diagnostics of thyroid cancer Bela Bendlova, Sarka Dvorakova, Vlasta Sykorova, Eliska Vaclavikova, Tereza Halkova, Josef Vcelak Dept. of Molecular Endocrinology, Institute of Endocrinology, Prague Thyroid carcinomas Parafollicular cell Medullary MTC < 10% Follicular cell Papillary PTC > 80% Follicular FTC 10-20% Anaplastic ATC 2-5% Incidence 1986 Chernobyl 26. 4. 1986 Causes of increasing incidence of thyroid cancer, especially PTC: Improvement of diagnosis, microcarcinoma Changes in diagnosis Over-supply iodine Chernobyl accident (26 April 1986) Genetics of thyroid carcinomas Proto-oncogenes and tumor-suppresor genes Chromosomal rearrangements: RET/PTC, NTRK1, PAX8/PPARγ, BRAF/AKAP9 Point mutations: Germ-line mutations in the RET gene in FMTC and MEN2 syndromes Somatic mutations in the BRAF and RAS genes, in PDTC and ATC also TP53, CTNNB1, PIK3CA, PTEN and AKT1 Factors in the development of DTC Landa I , Robledo M J Mol Endocrinal 2011;47:R43-R58 Genetic markers Diagnosis of disease More accurate prognosis Prediction of treatment reaction Target gene therapy Target therapy – inhibitors of tyrosine kinases VANDETANIB Keefe S M et al. Clin Cancer Res 2010;16:778-783 Genetics of PTC Extracellular space Cytoplasm RET/PTC Growth factor Tyrosine kinase receptor PTEN mutation TP NTRK1 rearrangement rearrangement RAS mutation Ras met amplification BRAF mutation Raf AKAP9/BRAF rearrangement MAPK Nucleus TP53 mutation Transcription factor Sample cohorts Fresh frozen thyroid samples Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, 1st Faculty of Medicine and Faculty Hospital Motol, Charles University, Prague Department of Surgery, 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Na Homolce Hospital, Prague Paraffin embedded formalin-fixed samples The Fingerland Department of Pathology, Hradec Kralove Institute of Pathology, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague Institute of Pathology and Laboratory of Molecular Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Palacky University, Olomouc Fine needle aspiration biopsies from Institute of Endocrinology Peripheral blood samples of healthy controls Molecular-genetic analysis: 234 PTC, 6 FTC, 1 FTA, 8 PDTC, 3 ATC, 23 MTC 172 healthy controls Clinicopathological characteristics sex age tumor size histological variant of PTC tumor invasion nodal metastasis distant metastasis multifocality of tumor encapsulation angioinvasion TNM stage recurrence Papillary structures Methods Izolation of NK RNA Trizol DNA Trizol, kit RNA → cDNA Real Time PCR PCR PCR Genotyping Sequencing Elektroforesis GAPDH PAX8 EC RET TK RET RET/PTC1 RET/PTC3 RET polymorphisms A432A – exon 7 G691S – exon 11 L769L – exon 13 S836S – exon 14 S904S – exon 15 RET BRAF – exon 15 H-RAS – exon 1 and 2 K-RAS – exon 1 and 2 N-RAS – exon 1 and 2 Results – RET/PTC RET/PTC rearrangements • 26 RET/PTC from 101 PTC (25.5 %): 2 RET/PTC1, 2 RET/PTC3 and 22 RET/PTCX RET/PTC1 • Male, 19 years, T1N0M0, multifocal PTC without a capsule and invasion, diffuse sclerosing variant, 17 months without recurrence • Female, 33 years, T1N1M0, unifocal encapsulated PTC without invasion, classic variant, 18 months without recurrence RET/PTC3 • Female, 12 years, T3N1M1, unifocal PTC without a capsule, with invasion into adjacent tissue and vessels, mixed follicular/papillary type, 39 months without recurrence • Female, 43 year, T3N0M0, multifocal PTC, follicular variant, 20 months without recurrence Results: PTC – RET polymorphisms Polymorphisms of RET gene 234 PTC vs. 172 controls p = 0.02 101 PTC – differences in exon 7 and 13 in relation to RET/PTC and sex of patients risk alelles – major alelle G (exon 7) and minor alelle G (exon 13) carriers of the risk haplotypes (GGGCC and GGGTC) – 2 times higher risk of RET/PTC rearrangements p = 0.04 Male Female Results – BRAF mutation detected in 81 of 242 PTC patients (33.5 %), in one of 6 poorly differentiated carcinomas (16.7 %), in one anaplastic carcinoma and in none of 23 MTC the impact of Chernobyl accident – re trospective study (47 years) 17 100 80 22 10 5 60 4 20 1991-1995 60 50 7 11 40 53 58 31 23 1 BRAF (%) Prevalence (%) 70 1986-1990 2001-2005 40 2006-2007 30 1996-2000 20 20 06 -2 00 7 20 01 -2 00 5 19 96 -2 00 0 19 91 -1 99 5 19 86 -1 99 0 Be fo r e 19 86 0 10 Before 1986 0 30 35 40 45 50 Age (median of years) 55 60 65 Results – BRAF mutation BRAF mutation is associated with a higher age at diagnosis (p = 0.049) a histologic variant (p = 0.001) (46.4 % classic vs. 13.2 % follicular variant) a greater tumor size (p = 0.041) with more agressive behavior of tumor presence of nodal metastasis (p = 0.029) more advanced TNM stage (p = 0.014) recurrence of disease (p = 0.008) Results – RAS mutations Gene Exon Alteration Codon Patient H-RAS 2 V44M GTG-ATG A C51Y TGC-TAC B L79L CTG-TTG B 1 E3K GAA-AAA A 2 Y40Y TAC-TAT C T50I ACC-ATC D L56L CTC-CTT D G60G GGT-GGA E G60G GGT-GGC F Q61K CAA-AAA E, F Q22Q CAG-CAA G Q22X CAG-TAG H Q61R CAA-CGA I, J, K, L A66T GCC-ACC C D69D GAC-GAT G E76K GAA-AAA C K-RAS N-RAS 1 2 98 samples – 83 PTC (56 FV PTC, 11 CV PTC, 14 mixed, 2 rare variants), 7 FTC, 1 FTA, 3 ATC, 4 PDTC In six patients detected mutation in codon 61 of N-RAS gene and K-RAS gene (aktivating domain) Found other silent, nonsense and missense genetic changes All genetic changes detected in follicular variant of PTC In silico analysis shows possible pathogenicity of some missense mutations (p.Cys51Tyr, p.Glu3Lys), that needs to be confirmed MTC and RET proto-oncogene • located on chromosome 10q11.2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Cadherin-like domain 8 9 10 11 12 Cysteine-rich region 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Tyrosine kinase domains Extracellular domain Intracellular domain Transmembrane region Activating germ-line mutations FMTC, MEN 2A, MEN 2B Activating somatic mutations Sporadic MTC Inactivating mutations Hirschsprung disease 20 21 Genetic screening of the RET gene Patient with MTC DNA analysis (blood, tumor) Mutation detected only in a tumor Mutation in blood and a tumor MTC sporadic MTC familial DNA analysis in all at-risk family members Prophylactic total thyroidectomy Mutation detected No mutation detected Biochemical screening Excluded from screening RET germ-line mutations in MTC patients 1 2 3 4 Arg321Gly 1x 5 6 7 8 Cys609Tyr 1x Cys611Arg 1x Cys611Tyr 1x 9 10 11 12 14 15 16 17 Cys634Ser 1x Cys634Phe 1x Leu790Phe 1x Tyr791Phe 3x Val804Leu 1x Val804Met 4x Cys634Trp 1x Glu768Asp 1x Tyr791Phe 2x Val804Met 1x Cys618Arg 1x Cys620Phe 1x Cys620Arg 1x 13 Cys634Arg 8x Cys634Tyr 1x Cys634Ser 2x 18 19 20 21 Met918Thr 9x Tyr791Phe 1x Tyr791Phe 1x spor. MTC FMTC MEN2A MEN2B Total Tested index patients 340 12 14 9 375 Mutation detected 14 (4%) 7 (58%) 13 (93%) 9 (100%) Tested family members 202 61 69 20 352 Mutation detected 13 19 25 3 60 Excluded from screening 20 20 43 17 100 RET germ-line mutations in HSCR patients 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Pro566Leu 1x Ala373Val 1x 11 12 13 del603(A) 14 15 16 Ser649Leu 2x Cys609Tyr 1x Cys620Arg 2x 17 18 19 20 Tyr791Phe 8x Gly798Ser 1x Exon Mutation Detected HSCR phenotype Dual phenotypic RET mutations Exon 10 Cys609Tyr 1x TCA Exon 10 Cys620Arg 2x TCA RET mutations typical for MTC Exon 11 Ser649Leu 2x 1x TCA, 1x RS Exon 13 Tyr791Phe 8x 2x TCA, 6x RS Novel RET mutations with unknown function Exon 6 Ala373Val 1x RS Exon 9 Pro566Leu 1x TCA Exon 10 del603(A) 1x TCA Exon 13 Gly798Ser 1x TCA 17x 9x TCA, 8x RS Total 156 patients 21 Haplotypes - MTC 1 – A45A (G/A) 2 – A432A (G/A) 3 – G691S (G/A) 4 – L769L (T/G) 5 – S836S (C/T) 6 – IVS14-24G>A 7 – S904S (C/G) Control cohort p = 0.003 Patients Publications Dvorakova S, Vaclavikova E, Sykorova V, Duskova J, Vlcek P, Ryska A, Novak Z, Bendlova B 2006 New multiple somatic mutations in the RET proto-oncogene associated with a sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 16:311–316. Bendlová B, Dvořáková S, Václavíková E, Sýkorová V, Vlček P, Škába R 2006 Nádory štítné žlázy a Hirschsprungova choroba – 10leté zkušenosti s molekulárně-genetickým testováním RET protookogenu. Vnitř Lek 52:926–934. Sýkorová V, Dvořáková Š, Kodetová D, Astl J, Ryška A, Dušková J, Vlček P, Novák Z, Bendlová B 2007 Genetické příčiny vzniku papilárního karcinomu štítné žlázy Diab Metab Endokrinol Výživa 1:30–35. Dvorakova S, Vaclavikova E, Sykorova V, Vcelak J, Novak Z, Duskova J, Ryska A, Laco J, Cap J, Kodetova D, Kodet R, Krskova L, Vlcek P, Astl J, Vesely D, Bendlova B 2008 Somatic mutations in the RET proto-oncogene in sporadic medullary thyroid carcinomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 284(1–2):21–27. Vaclavikova E, Dvorakova S, Sykorova V, Bilek R, Dvorakova K, Vlcek P, Skaba R, Zelinka T, Bendlova B 2009 RET mutation – Tyr791Phe – the genetic cause of different diseases derived from neural crest. Endocrine, 36(3):419–424. Sykorova V, Dvorakova S, Ryska A, Vcelak J, Vaclavikova E, Laco J, Kodetova D, Kodet R, Cibula A, Duskova J, Hlobilkova A, Astl J, Vesely D, Betka J, Hoch J, Smutny S, Cap J, Vlcek P, Novak Z, Bendlova B 2010 BRAFV600E Mutation in the Pathogenesis of a Large Series of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in Czech Republic. J Endocrinol Invest, 33:318-324. Acknowledgement Institute of Endocrinology RNDr. Š. Dvořáková, Ph.D. Mgr. E. Václavíková Mgr. Tereza Hálková Mgr. Josef Včelák MUDr. Z. Novák, CSc. Doc. MUDr. J. Vrbíková, CSc. Department of Nuclear Medicine and Endocrinology, 2nd Faculty of Medicine and Faculty Hospital Motol, Prague Doc. MUDr. P. Vlček, CSc. Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, 1st Faculty of Medicine and Faculty Hospital Motol, Prague Doc. MUDr. J. Astl, CSc., MUDr. J. Veselý, Prof. MUDr. J. Betka, DrSc. Department of Surgery, 2nd Faculty of Medicine and Faculty Hospital Motol, Charles University, Prague Prof. MUDr. J. Hoch, CSc., MUDr. S. Smutný Institute of Pathology, 1st Faculty of Medicine and Faculty Hospital Motol, Charles University, Prague Prim. MUDr. D. Kodetová, Prof. MUDr. R. Kodet, CSc., Mgr. A. Cibula The Fingerland Department of Pathology, Faculty Hospital Hradec Kralove Prof. MUDr. A. Ryška, CSc., MUDr. J. Laco Institute of Pathology and IPVZ, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague Doc. MUDr. J. Dušková, CSc. Institute of Pathology and Department of Molecular Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Palacky University, Olomouc MUDr. A. Hlobilková, Ph.D. Department of Endocrinology, Faculty Hospital Hradec Kralove Prof. MUDr. J. Čáp, CSc. Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Na Homolce Hospital, Prague MUDr. J. Lukáš Supported by grant project IGA MH CR NR/9165-3 Thank you for your attention
Podobné dokumenty
K-RAS - Fingerlandův ústav patologie
 Dvorakova S, Vaclavikova E, Sykorova V, Duskova J, Vlcek P, Ryska A, Novak Z, Bendlova B 2006 New
multiple somatic mutations in the RET proto-oncogene associated with a sporadic medullary thyroid
c...
Dvorakova S, Vaclavikova E, Sykorova V, Duskova J, Vlcek P, Ryska A, Novak Z, Bendlova B 2006 New
multiple somatic mutations in the RET proto-oncogene associated with a sporadic medullary thyroid
c...
Hemostáza 1/ Vazokonstrikce – 2/ činnost krevních destiček
 Aktivovaný parciální tromboplastinový čas (aPTT) plazma z centrifugovane krve, dekalcifikované natriumcitrátem, přidává se kaolin (aktivuje faktory fáze kontaktu –
XII) a směs fosfolipidů (kefalin ...
Aktivovaný parciální tromboplastinový čas (aPTT) plazma z centrifugovane krve, dekalcifikované natriumcitrátem, přidává se kaolin (aktivuje faktory fáze kontaktu –
XII) a směs fosfolipidů (kefalin ...
Dny dětské endokrinologie 2007: „Kazuistiky z dětské
 Intoxikace glibenclamidem tedy u Filipa vedla k protrahovanému hypoglykemickému kómatu. U
Filipa se během další hospitalizace projevila sekundární epilepsie a bylo zahájeno podávání
antiepileptické...
Intoxikace glibenclamidem tedy u Filipa vedla k protrahovanému hypoglykemickému kómatu. U
Filipa se během další hospitalizace projevila sekundární epilepsie a bylo zahájeno podávání
antiepileptické...
Výroční zpráva - Endokrinologický ústav
 nových metod, podílí se na klinickém hodnocení léčiv a ověřování prostředků
zdravotnické techniky s cílem prokázat jejich účinnost, bezpečnost a kvalitu. Získané
výsledky šíří prostřednictvím výuky...
nových metod, podílí se na klinickém hodnocení léčiv a ověřování prostředků
zdravotnické techniky s cílem prokázat jejich účinnost, bezpečnost a kvalitu. Získané
výsledky šíří prostřednictvím výuky...
Přesné magnetické snímače a jejich aplikace
 snímací cívky antisériově na jednom jádře). Přesto obvykle konstrukce
gradiometru s dvěma samostatnými senzory a následným odečtením signálu
poskytují lepší výsledky (lepší stabilita). Obsáhlý popi...
snímací cívky antisériově na jednom jádře). Přesto obvykle konstrukce
gradiometru s dvěma samostatnými senzory a následným odečtením signálu
poskytují lepší výsledky (lepší stabilita). Obsáhlý popi...
 Elektroda
Elektroda
 onkologii.
I: Radiofyzika a obecná radioterapie
onkologii.
I: Radiofyzika a obecná radioterapie